- Speed up a slow heart rhythm.
- Help control an abnormal or fast heart rhythm.
- Make sure the ventricles contract normally if the atria are quivering instead of beating with a normal rhythm (a condition called atrial fibrillation).
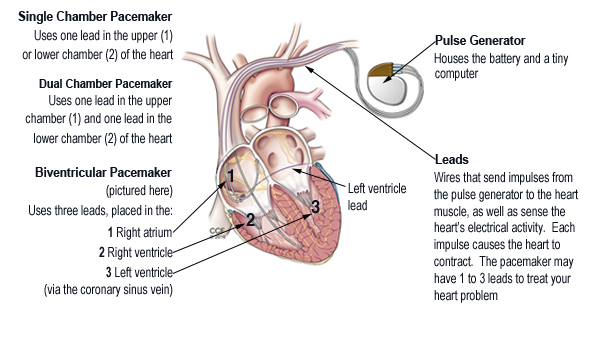
- Coordinate the electrical signaling between the upper and lower chambers of the heart.
- Coordinate the electrical signaling between the ventricles.
- Pacemakers that do this are called cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT) devices. CRT devices are used to treat heart failure.
- Prevent dangerous arrhythmias caused by a disorder called long QT syndrome.
Pacemakers also can monitor and record your heart's electrical activity and heart rhythm. Newer pacemakers can monitor your blood temperature, breathing rate, and other factors and adjust your heart rate to changes in your activity.
Pacemakers can be temporary or permanent. Temporary pacemakers are used to treat temporary heartbeat problems, such as a slow heartbeat that's caused by a heart attack, heart surgery, or an overdose of medicine.
Temporary pacemakers also are used during emergencies. They're used until a permanent pacemaker can be implanted or until the temporary condition goes away. If you have a temporary pacemaker, you'll stay in a hospital as long as the device is in place.
Permanent pacemakers are used to control long-term heart rhythm problems. This article mainly discusses permanent pacemakers, unless stated otherwise.
Doctors also treat arrhythmias with another device called an implantable cardioverter defibrillator (ICD). An ICD is similar to a pacemaker. However, besides using low-energy electrical pulses, an ICD also can use high-energy electrical pulses to treat certain dangerous arrhythmias.
What Is a Pacemaker?
A pacemaker is a small device that's placed in the chest or abdomen to help control abnormal heart rhythms. This device uses electrical pulses to prompt the heart to beat at a normal rate.
Pacemakers are used to treat arrhythmias (ah-RITH-me-ahs). Arrhythmias are problems with the rate or rhythm of the heartbeat. During an arrhythmia, the heart can beat too fast, too slow, or with an irregular rhythm.
A heartbeat that's too fast is called tachycardia (TAK-ih-KAR-de-ah). A heartbeat that's too slow is called bradycardia (bray-de-KAR-de-ah).
During an arrhythmia, the heart may not be able to pump enough blood to the body. This may cause symptoms such as fatigue (tiredness), shortness of breath, or fainting. Severe arrhythmias can damage the body's vital organs and may even cause loss of consciousness or death.
A pacemaker can relieve some arrhythmia symptoms, such as fatigue and fainting. A pacemaker also can help a person who has abnormal heart rhythms resume a more active lifestyle.
For more information: http://bit.ly/GVf9gu







0 comments:
Post a Comment